Description
A solid-state relay SSR is an electronic switching device that uses semiconductor components like thyristors, triacs, or transistors to perform switching operations. Unlike electromechanical relays that use mechanical contacts to switch circuits, solid-state relays use electronic components to achieve similar functionality. SSRs are widely used in various applications, including industrial automation, robotics, HVAC systems, and more. One of the primary advantages of SSRs is that they have no mechanical moving parts. This absence of physical contacts reduces wear and tear, enhances reliability, and results in longer operational lifespans. SSRs come in various voltage and current ratings to accommodate different load requirements. The input control of an SSR can be a DC voltage, a DC current, or a digital signal, depending on the type and design of the relay. SSRs offer benefits such as noise immunity, longer lifespan, high switching speeds, and reliability due to their lack of mechanical components.


































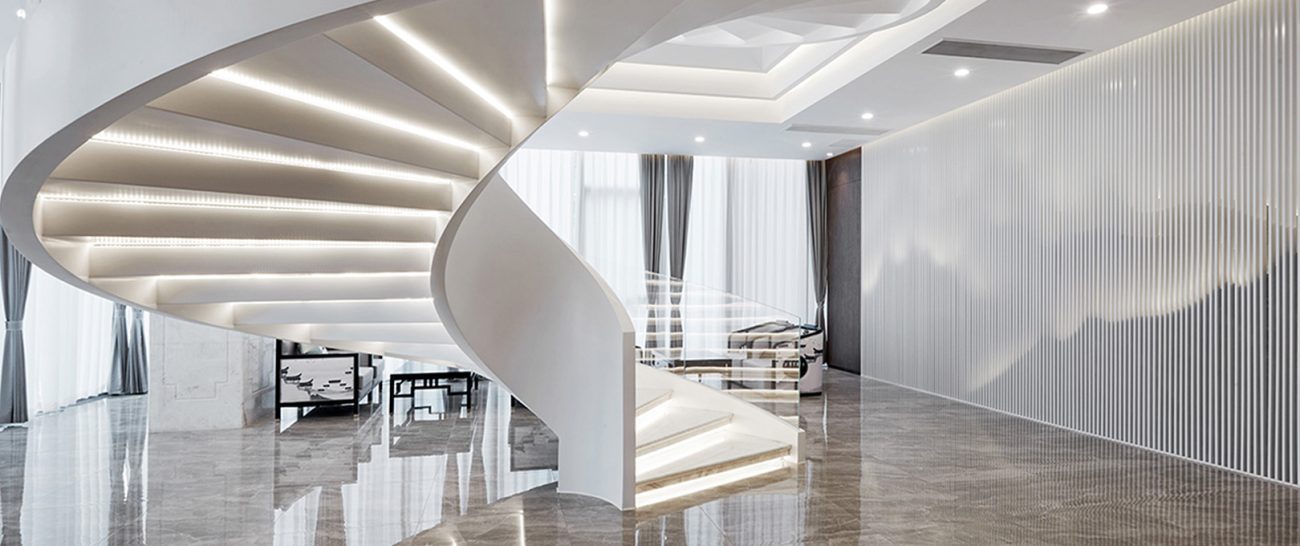
 Italian LUXURY Lighting
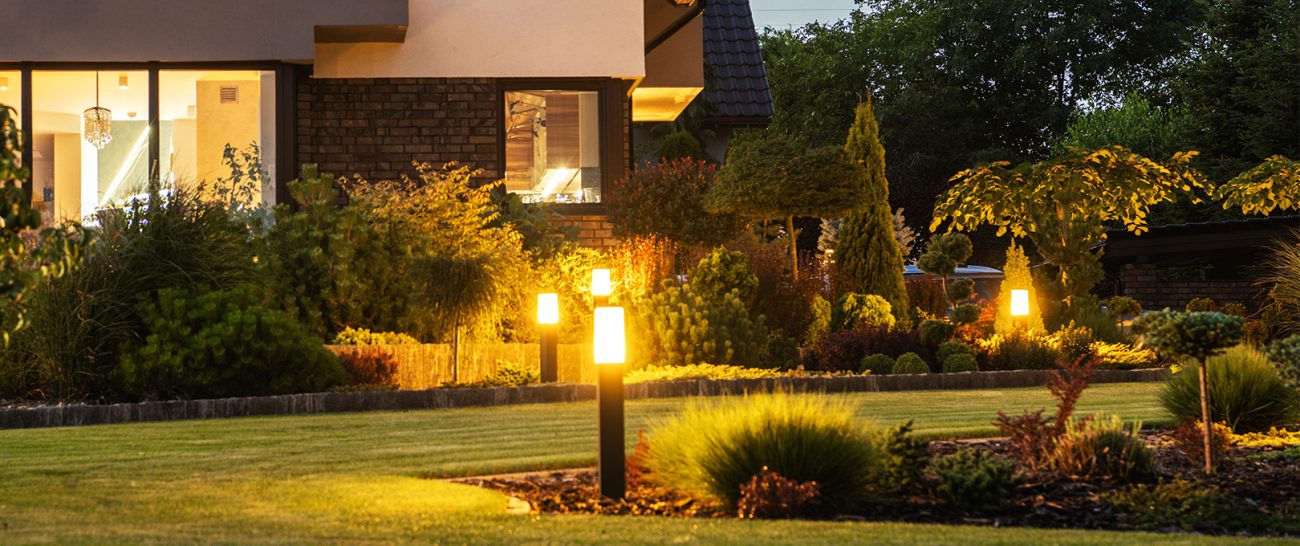
Italian LUXURY Lighting